SOLUTION
Operational Resilience
Put Resilience at the Core
of Everything You Do
Align with regulatory frameworks such as FCA, PRA, DORA, BCBS, and the Federal Reserve by building resilience directly into your operations.
From defining impact tolerances to testing recovery capabilities, you can protect customers and stakeholders with confidence.
• Continuity
Map the Customer Journey
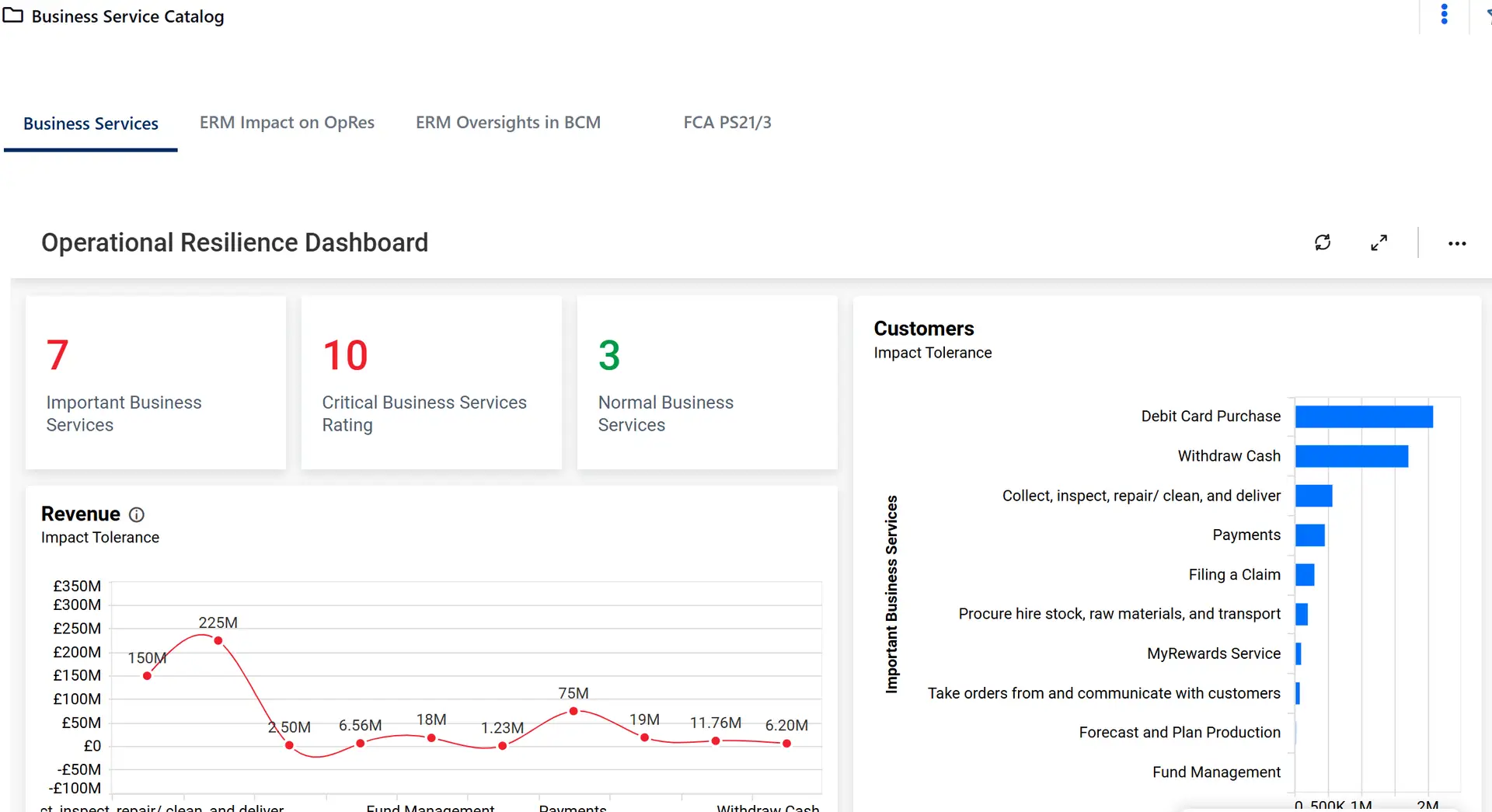
CLDigital 360 gives organizations the ability to maintain programs over time, even as the demands upon those programs change. By mapping business services to the underlying people, processes, technology, locations, and vendors, CLDigital 360 users build operational intelligence and insights that can be applied to any number of business and/or recovery strategies.
Download the Operational Resilience guide to learn more.
Deepen Your Understanding
of Critical Connections
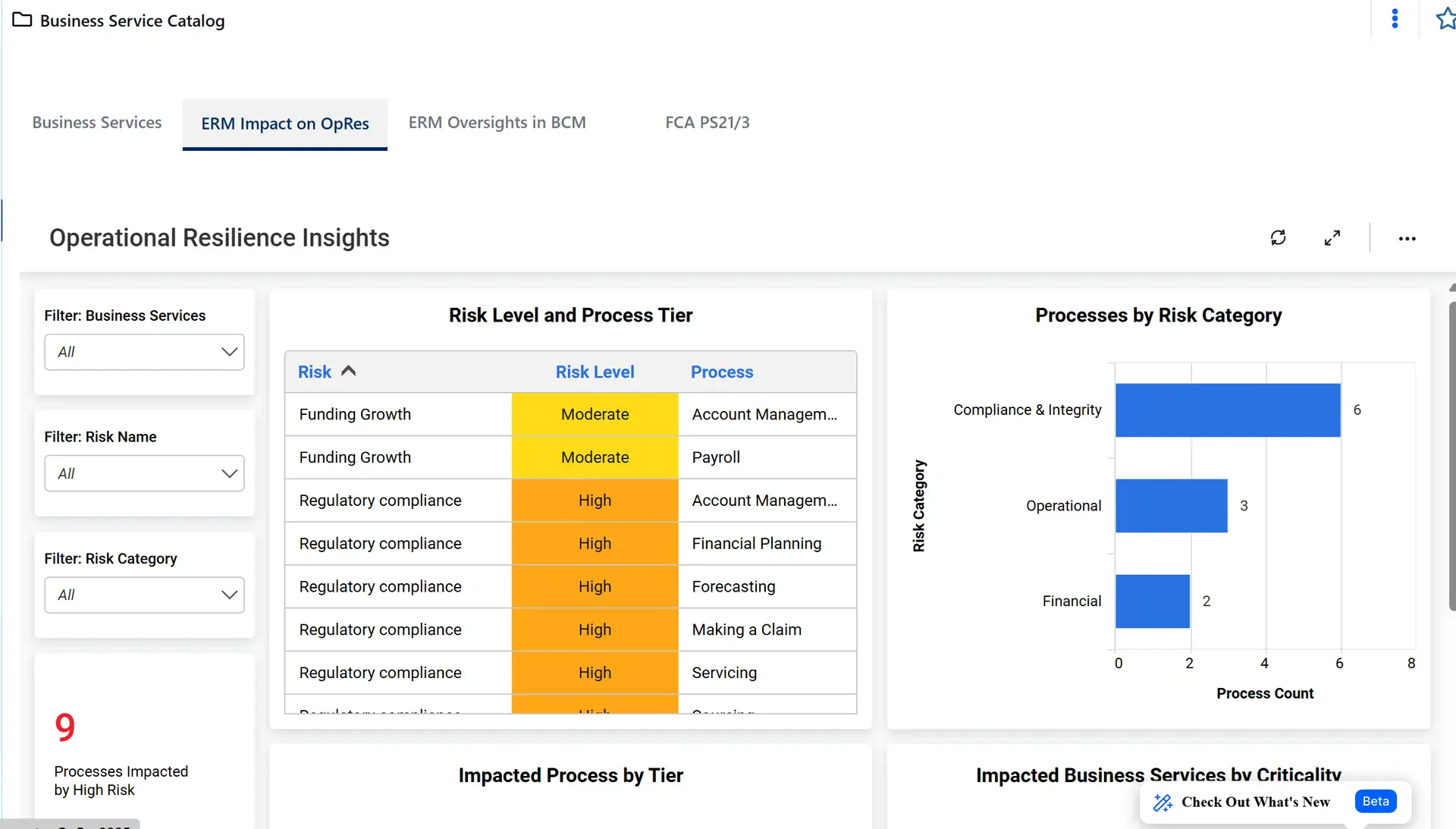
Go beyond surface-level monitoring with dashboards, dependency mapping, and scenario testing
These capabilities reveal hidden vulnerabilities, validate impact tolerances, and confirm your strategies will hold up under real-world stress.
With this visibility, you can dismantle silos, pinpoint dependencies, and make informed decisions that reduce disruption and strengthen oversight.
BENEFITS
Accelerated Readiness
Cut Initiative Time
Save $1.5M Annually
Maintain Critical Services
FAQ
Solution FAQs
What is Operational Resilience?
What are the key functionalities of Operational Resilience?
The key functionalities include risk integration, continuity planning, resilience testing, scenario modeling, third-party monitoring, and compliance reporting.
What are the five pillars of Operational Resilience?
To achieve operational resilience, an organization must look beyond simple disaster recovery and instead build a system that can absorb shocks and adapt to changing circumstances.
1. Risk Identification and Management
This pillar serves as the foundation for resilience by proactively identifying and mapping internal and external threats that could disrupt critical business services. Rather than just listing generic risks, effective management involves “impact mapping”—understanding how a failure in one third-party vendor or a single data point could cascade through the entire organization. By identifying these vulnerabilities early, companies can prioritize resources toward the most high-impact areas.
2. Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Business continuity focuses on the “how-to” of maintaining operations during a disruption. It involves setting Tolerance for Disruption levels, which define the maximum amount of time a service can be down before causing irreparable harm to customers or the market. A strong BCP includes detailed playbooks that outline alternative strategies, processes, and procedures to keep essential services running while primary systems are being restored.
3. IT Resilience
IT resilience is the technical ability of an organization’s digital assets and infrastructure to remain available and secure under stress. This goes beyond standard backups to include high-availability architecture, “self-healing” cloud systems, and robust cybersecurity protocols. In an era of constant cyber threats, this pillar ensures that data remains intact and that digital platforms can failover to secondary sites without significant data loss or downtime, which may have rippling impacts for customers or the market.
4. Crisis Management and Response
While BCP focuses on the process, Crisis Management focuses on the people and communication. This pillar establishes the command structure and communication channels needed to make rapid, high-stakes decisions during an emergency. It ensures that stakeholders—including employees, regulators, and the public—receive clear, accurate information, which helps preserve the organization’s reputation and trust even when physical or digital operations are compromised.
5. Adaptive Governance and Culture
Resilience is ultimately a capability and a muscle that needs conditioning. This pillar ensures that leadership is actively involved in resilience oversight and that the organization’s culture values agility over rigid adherence to old protocols. Adaptive governance involves continuous learning; after every “near miss” or minor disruption, the organization conducts a post-mortem to update its strategies. This creates a feedback loop where the company becomes stronger and more prepared with every challenge it faces.
What are the benefits of Operational Resilience?
What are the challenges of Operational Resilience?
GET STARTED
Let's Connect
Discover how our platform can help you achieve better outcomes and you prepare for what’s next in risk and resilience.